Environmental Considerations in Offshore Wind Development
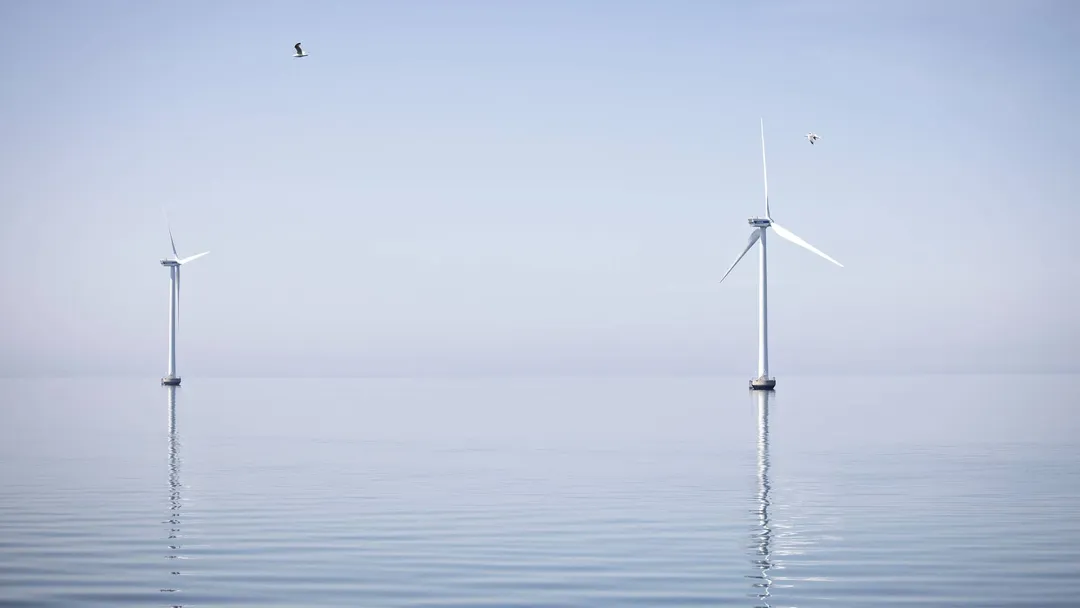
The development of offshore wind farms represents a critical component of the global transition to renewable energy. However, it is essential to balance this progress with environmental protection to ensure sustainable development. A prime example of this balance can be seen in the recent cancellation of Denmark's Omo Syd offshore wind project due to its location within a designated bird sanctuary.
The Omo Syd Project Cancellation
The Omo Syd offshore wind project, developed by European Energy, had been in planning for over a decade and received environmental impact assessment (EIA) approval in 2020. However, in January 2024, the Danish government decided to designate the project area as a Natura 2000 bird sanctuary, effectively halting the development. The primary reasons for the cancellation were the project's potential impact on bird populations and the new height restrictions for wind turbines, which exceeded the current technological standards.
Importance of Environmental Impact Assessments (EIA)
Environmental impact assessments are crucial in identifying and mitigating potential adverse effects of wind farm projects on the environment. EIAs evaluate factors such as wildlife habitats, migration patterns, and marine ecosystems. In the case of Omo Syd, the EIA initially allowed the project to proceed but did not foresee the subsequent designation of the area as a bird sanctuary. This underscores the dynamic nature of environmental protection, where regulations and ecological priorities can evolve.
Sustainable Practices in Offshore Wind Development
Sustainable practices in offshore wind development involve careful site selection, continuous environmental monitoring, and adaptive management strategies. These practices aim to minimize ecological disruption and promote coexistence with natural habitats. For instance:
- Adaptive Management: Implementing adaptive management strategies allows developers to modify their operations based on ongoing environmental monitoring and feedback. This approach helps in addressing unforeseen environmental impacts promptly.
- Technological Innovations: Advances in wind turbine technology, such as quieter turbines and improved foundation designs, reduce the environmental footprint of wind farms. Floating wind turbines, for example, can be deployed in deeper waters, minimizing disruption to coastal and seabed ecosystems.
- Collaborative Planning: Engaging stakeholders, including environmental groups, local communities, and regulatory bodies, ensures that all potential environmental impacts are considered and addressed. Collaborative planning fosters transparency and builds public trust in renewable energy projects.
Conclusion
The cancellation of the Omo Syd project highlights the complexities and challenges in balancing renewable energy development with environmental protection. While the need for clean energy is urgent, it must not come at the expense of critical habitats and biodiversity. Environmental impact assessments and sustainable practices are essential tools in achieving this balance, ensuring that the transition to renewable energy is both ecologically responsible and socially acceptable. By learning from these experiences and continually improving our approaches, we can develop offshore wind projects that contribute to a sustainable and resilient future.